Author: Jimmy Li Qiu Road (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. practicing control instruments Wang Jun Shanghai Le Ze Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd. Jin Yan
The cutting fluid plays an important role in the metal cutting and grinding process. The selection of a suitable metal cutting fluid can reduce the cutting temperature by 60-150 ° C, reduce the surface roughness of 1 to 2, and reduce the cutting resistance by 15% to 30%. , double the life of the tool and the grinding wheel. The cutting and ash can be washed away from the cutting zone, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality, so the cutting fluid is widely used in machining. However, in the normal machining process, the cutting fluid often has many problems such as deterioration, odor, corrosion, foaming, skin irritation of the user, etc. These problems are mainly caused by the accumulation of impurities in the cutting fluid, the accumulation of various types of grease, and A large increase in bacteria in the cutting fluid causes the odor of the cutting fluid.
1. Recirculation and reduction of cutting fluid
(1) Conventional treatment methods and shortages of cutting fluids In view of the problems in the use of the above cutting fluids, most companies currently take the following measures: 1 Regularly add tap water and cutting fluid concentrate to maintain the concentration and pH of the cutting fluid. The value is within the recommended range. 2 Add a fungicide in specific situations. 3 Increase the oil slinger to remove oil slick and related impurities. 4 Increase the particle filter device and periodically filter the cutting fluid. In the past half a year, all the cutting fluids were completely replaced and entrusted to professional environmental protection companies.
However, the above measures are mainly for the daily maintenance of the cutting fluid. The cutting fluid is not effectively treated, and the waste cutting fluid is not reused. Therefore, the cutting fluid must be completely replaced in about 6 months. Liquid discharge is thus produced.
According to the relevant provisions of the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Wastes, the cutting fluids discharged by mechanical processing are classified as hazardous wastes and are classified as waste emulsions in the National Catalogue of Hazardous Wastes under the number HW09. With the continuous improvement of social environmental awareness, China's relevant environmental protection departments encourage enterprises to develop circular economy, realize the recycling of hazardous waste, and realize the reuse of hazardous waste through the application of advanced recycling technology, thus greatly reducing the amount of hazardous waste disposal.
If the re-use and reduction of cutting fluid waste can be realized, it will not only have certain economic benefits for the machining enterprises, but more importantly, it has great environmental benefits.
(2) Principle of reduction and re-use of cutting fluid According to the above reasons, if there are techniques to remove the tiny impurities, grease and bacteria in the waste cutting fluid, to avoid spoilage and deterioration, and to ensure that the cutting fluid is restored to the new cutting The liquid has the same high cleanliness, can be recycled to the specified concentration and pH range, and can be recycled to the daily use state.
A technology derived from the French Atomic Energy Research Institute (CEA), the membrane treatment technology, makes the re-use of cutting fluids a reality. Since ceramic membranes have a good demulsification effect on cutting emulsion wastewater, they have been widely used in recent years.
The system principle is shown in Figure 1:
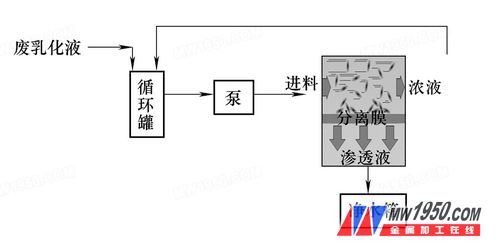
Analysis: 1 feed, is a waste cutting fluid, containing tiny impurities, grease and bacteria. 2 separation membrane is the core component of the system. The membrane contains a separation layer that completely blocks the tiny bacteria. 3 Permeate is a cutting fluid that removes contaminants such as minute impurities, grease, and bacteria, that is, a cutting fluid that has been purified. 4 concentrated liquid, is a waste cutting fluid with higher concentration of impurities and bacteria.
System working process description: 1 waste cutting fluid is discharged into the system circulation tank first. 2 The waste cutting fluid in the circulation tank enters the separation system with a certain pressure through the pump. The waste cutting fluid flows parallel to the membrane surface under the push of the pump. Due to a certain pressure (0.1-0.3 MPa), water and organic matter can enter the clean water tank through the separation membrane. All impurities and bacteria are intercepted by the separation membrane. This achieves efficient separation of impurities and bacteria. 3 In order to increase the recovery rate of the entire system, the concentrate is returned to the circulation tank. Until the end of the entire system operation, 3% to 10% of the concentrated liquid is finally discharged from the system. 4 The recovery rate of the system is 90% to 97%, and the specific recovery value is related to the nature of the waste cutting fluid of each enterprise.
Excellent performance description of the patented ingredient formulation and advanced production process in the separation module: 1 Material: TiO2/ZrO2 (titanium dioxide/zirconia). 2 separation accuracy: 25 ~ 50nm. 3 temperature resistance up to 300 ° C, can be sterilized by steam. 4 acid and alkali and chemicals: withstand pH 0 ~ 14, not subject to chemical corrosion. 5 solvent resistance: disinfection with oxidant. 6 Excellent mechanical strength: bursting pressure >9MPa, can be sterilized by autoclave. 7Safe, environmentally friendly: FDA certified.
Ultra-fine filtering accuracy is the guarantee for safe and effective filtration of the system. Bacteria are considered to be the smallest pollution factor in waste cutting fluid contaminants. The individual bacteria are small. Most bacteria have a diameter of 0.5 to 5 μm. The smallest bacteria known to be only 0.2 μm, and the separation accuracy of this treatment method is 25 to 50 nm, it can fundamentally and effectively treat the bacteria in the waste cutting fluid, and at the same time greatly reduce the amount of hazardous waste generated, which effectively promotes the ecological environment.

Figure 2 Comparison of the cutting fluid before and after treatment: 1 new cutting fluid A means: according to the cutting fluid usage requirements, the cutting fluid is added with water to match the cutting fluid with the specified concentration. The recommended concentration is 8% to 10%. , pH 9 ~ 9.5. 2 Waste cutting fluid B refers to: the cutting fluid waste liquid to be treated about half a year after the processing machine tool is operated. 3 After the treatment, the produced water C refers to the produced water after the waste liquid is treated by the above purification system, that is, the purified cutting fluid. 4 After the treatment, the waste concentrate D refers to the waste concentrate after the waste liquid is treated by the above purification system.
A German-owned enterprise has multiple DMG machine tools , mostly 125P, 80U, 60U, Maha and other machining centers, mainly based on metal carbon steel, alloy steel and aluminum cutting, using Master E905 emulsion for cooling lubrication. The cutting fluid is completely replaced once every six months.
(1) Processing result of cutting fluid waste liquid The waste cutting fluid is reprocessed by the above cutting fluid recycling technology, and the result of the processing is shown in Fig. 2. The test data pairs are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Comparison table of separated water production test data 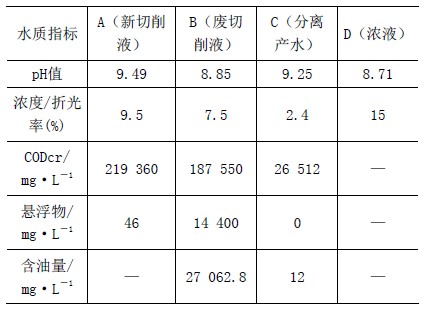
Among them: 1 concentration / refractive index: refractive index is one of the most important physical constants of organic compounds, can be accurately and conveniently detected, as a standard for the purity of liquid substances, can be easily detected using a refractometer. 2COD stands for chemical oxygen demand: It refers to the amount of oxidant consumed by reducing substances in 1L water sample under certain conditions. It is expressed in terms of oxygen concentration (in mg/L) and is the assessment of water pollution. One of the important comprehensive indicators. The larger the value of COD, the more serious the water pollution. The COD in the cutting fluid is mainly composed of triethanolamine, a surfactant, a boric acid compound, a preservative, a bactericide, and oil and impurities brought in during the cutting process. 3 Suspended matter means that the retained particulate impurities can be filtered by a 0.45 μm filter. 4 oil content: mineral oil concentration.
(2) Analysis of the processing results of the cutting fluid waste liquid? According to the above data comparison, the treated separated separated water can be seen: 1 The pH value rises and returns to the permitted use interval. 2 mixture concentration / refractive index decreased. 3 The suspension is completely removed. 4 The concentration of mineral oil is basically removed. 5CODcr value is greatly reduced. This is because the pollutant oil, bacteria and impurities in the cutting fluid are removed by filtration, while the main raw material surfactant, preservative and bactericide of the cutting fluid are retained. Therefore, the quality of the filtered produced water is in full compliance with the water quality requirements for the recycling of the cutting fluid.
(3) After the cutting fluid waste liquid is purified, the water is reused. The effective concentration of the cutting fluid after purification is relatively low, and it is necessary to add the cutting fluid concentrate for re-adjusting the formula.
The above-mentioned 2.4% of the produced water obtained by the purification system, 50 mL + 50 mL of water + 10 mL of the cutting fluid concentrate is newly matched to the cutting fluid E to be used, and the same data index is detected.
From the comparative data in Table 2, the treated water can be added with a new concentrate, and if necessary, some tap water can be added to re-equip it into a new cutting fluid that meets the requirements.
Table 2 Comparison of test data of new water-cutting cutting fluid 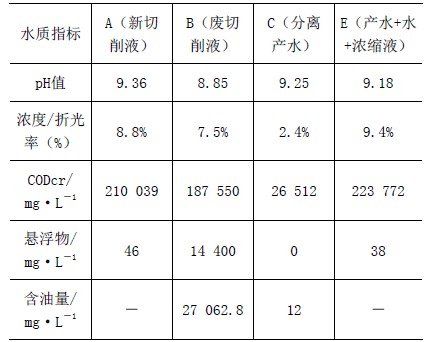
In Figure 3, A is matched with the cutting fluid. The cutting fluid is mixed with water to form the cutting fluid with the specified concentration. E is 2.4% of the cutting fluid. The treated liquid is treated with C50mL + 50mL tap water + 10mL cutting fluid. Cutting fluid.

Figure 3 Comparison of new water production cutting fluid
According to the comparison of the test data, the index of the cutting fluid E is basically close to the indexes of A (new cutting fluid), and the basic performance of the cutting fluid is maintained. At present, the new cutting fluid according to this method has been reused in the machine tool and the performance is stable.
3. Analysis of economic benefits of cutting fluid recycling
At present, if the annual waste liquid amount of the enterprise is less than 10t, the average processing cost of the waste cutting fluid is about 5 yuan/kg, and the new cutting fluid concentrate is about 30 yuan/kg, with a five-axis machining center with about 600L. The water tank, when working normally, the water tank contains about 550L of cutting fluid, and the cutting fluid is completely replaced twice a year. The cost of replacing the cutting fluid compared with the old and new treatment methods is shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Comparison of economic and benefit analysis of new and old treatment methods for cutting fluid waste liquid 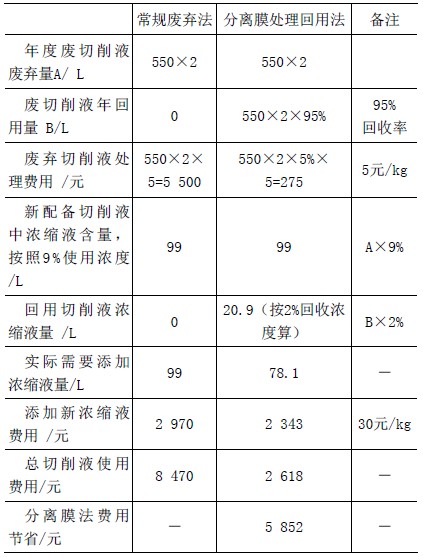
From the comparative data in Table 3, the average annual cost savings for a device is 5,852 yuan. At the same time, the amount of waste cutting fluid is greatly reduced, which greatly reduces the pressure on the society to handle hazardous waste, and has great environmental benefits.
Equipment investment: For a 600L water tank equipment, the design processing capacity is 600L/h, and the average equipment investment is 250,000 yuan/set. The core component separation membrane cost is 60,000 yuan/set, the service life is 4-5 years, and the equipment energy consumption is about 7.5kW, the daily maintenance cost is only the electricity cost and the labor cost of the separation membrane cleaning. That is, if an average of 16 600L capacity equipment needs to process the cutting fluid every year, the equipment investment can be recovered in 3 years.
On the other hand, because there are few enterprises with such a large amount of equipment, in the Yangtze River Delta, the processing equipment of such processing equipment enterprises is huge, and a single enterprise can purchase this by means of entrusted service or equipment leasing. Class services to achieve the purpose of reducing emissions and increasing efficiency.
4. Conclusion
In summary, the use of the separation membrane method to treat waste cutting fluid, the cutting fluid reuse and reduction treatment, has practical significance, on the one hand, considerable economic benefits, more importantly, has great environmental protection benefits, is a Application technology worth promoting.
Fesi Furnace Lining Carbon Paste
Fesi Furnace Lining Carbon Paste,Code Ramming Paste For Cac2,Furnace Lining Carbon Paste,Fesi Lining Carbon Paste
Pingluo Zhongxing Carbon Co.,Ltd , http://www.ztecarbon.com
