Abstract Note: Due to its low toxicity, nanodiamond is a promising contrast agent. (Singlenanodiamond: Single Crystal Nanodiamond, Aggregate: Aggregation) British researchers use common industrial nano...
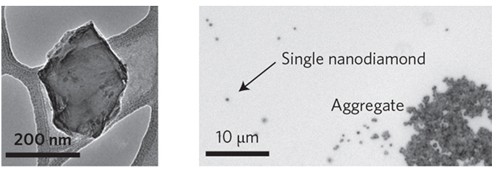
Note: Due to its low toxicity, nanodiamond is a promising contrast agent. (Single nanodiamond: single crystal nanodiamond, Aggregate: aggregate)
British researchers have used a common industrial nanodiamond to invent a new microscopic imaging technique for detecting live cells. Researchers believe the technology can effectively improve the effectiveness of medical research and treatment. Due to its low toxicity characteristics, nanodiamonds have extremely high medical imaging contrast agents and development prospects for drug delivery devices. However, many applications of nanodiamonds require a combination with a fluorophore, such as a nitrogen vacancy center, which fluoresces upon laser excitation. However, this method is expensive and inconvenient to control fluorescence.
Using the Raman scattering effect, non-fluorescent nanodiamonds can be analyzed. The continuous supply of light to the sample acts in conjunction with the covalent bond of the vibration: the scattered photons exhibit these covalent bond resonance frequencies. However, conventional Raman scattering is relatively weak, so the imaging time is relatively long and is a serious problem for a living tissue. Using two incident infrared lasers, anti-Stokes-Raman scattering can overcome this problem. The different frequencies between the two laser beams are the same as the vibration frequency of the chemical bonds, and all the covalent bonds in the phase are driven to amplify the signal and shorten the imaging time to present an image. These all benefit from nanodiamonds, which have a large number of identical covalent bonds.
Paola Borri of the University of Cardiff in the United Kingdom and colleagues used anti-Stokes-Raman scattering microscopy to observe their own set images of 70 to 150 nm diameter in water using nanodiamonds. From this image, the researchers calculated that the diamond has a diameter of at least 27 nm. Many medical nanoparticles are smaller, sometimes only 1 to 2 nanometers, but Borri believes that nanodiamonds have more room to play.
"When the target cells are reached, for example, cancer cells, the most important thing is that the nanodiamonds should not be too small to be expelled from the body," he said. “The most important thing is that we are now measuring a certain number of selected nanodiamond single crystal particles, which are related to the intensity of the anti-Stokes-Raman scattering signal. The size of the nanodiamond placed in the living cell is not measured. It may be related to fluorescence technology.†Researchers using human cells in the laboratory obtained clear images of diamonds without being destroyed by the test process.
Although larger particle diamonds have potential problems with lower surface area for drug delivery, Yury Gogotsi, a materials scientist at Drexel University, is still interested in the technology. 'Compared to previous methods, 5 nanometer diamond particles - it may become an effective means of delivery of therapeutic agents,' he said.
Using the Raman scattering effect, non-fluorescent nanodiamonds can be analyzed. The continuous supply of light to the sample acts in conjunction with the covalent bond of the vibration: the scattered photons exhibit these covalent bond resonance frequencies. However, conventional Raman scattering is relatively weak, so the imaging time is relatively long and is a serious problem for a living tissue. Using two incident infrared lasers, anti-Stokes-Raman scattering can overcome this problem. The different frequencies between the two laser beams are the same as the vibration frequency of the chemical bonds, and all the covalent bonds in the phase are driven to amplify the signal and shorten the imaging time to present an image. These all benefit from nanodiamonds, which have a large number of identical covalent bonds.
Paola Borri of the University of Cardiff in the United Kingdom and colleagues used anti-Stokes-Raman scattering microscopy to observe their own set images of 70 to 150 nm diameter in water using nanodiamonds. From this image, the researchers calculated that the diamond has a diameter of at least 27 nm. Many medical nanoparticles are smaller, sometimes only 1 to 2 nanometers, but Borri believes that nanodiamonds have more room to play.
"When the target cells are reached, for example, cancer cells, the most important thing is that the nanodiamonds should not be too small to be expelled from the body," he said. “The most important thing is that we are now measuring a certain number of selected nanodiamond single crystal particles, which are related to the intensity of the anti-Stokes-Raman scattering signal. The size of the nanodiamond placed in the living cell is not measured. It may be related to fluorescence technology.†Researchers using human cells in the laboratory obtained clear images of diamonds without being destroyed by the test process.
Although larger particle diamonds have potential problems with lower surface area for drug delivery, Yury Gogotsi, a materials scientist at Drexel University, is still interested in the technology. 'Compared to previous methods, 5 nanometer diamond particles - it may become an effective means of delivery of therapeutic agents,' he said.
YJCB is a leading manufacturer specialized in providing Measuring Spoons in China.
High quality with wide range of products, perfect for all of your baking needs.
We have many different Measuring Spoon Set, Measuring Spoons, Measuring Scoop, with different size, different material.
100% food grade, useful and durable. Make your baking life more convenience.
Easy cleaning and maintenance, Can be used safely in the baking.
We hope to cooperate with more customers for mutual development and benefits. Buyers are welcome to contact us!
Measuring Spoons
Measuring Spoon Set,Measuring Spoons,Measuring Scoop,Stainless Steel Measuring Spoons
Yangjiang YJCB Trade Co., Ltd , https://www.cbprokitchen.com
